5.20. Flight route section¶
Note
FlightRouteSectionParser
is responsible for parsing sections which provide information about route of a
single flight.
Route consists of separate points. Each point is defined on a single line.
Lines which start with TRIGGERS keyword indicate options for a point
which was defined in the previous line.
The output of the parser is a dictionary with a single item. It is accessible
by FLIGHT_ID_route key, where FLIGHT_ID is an ID of the flight which is
listed in Wing section. The value is a list of dictionaries, where each
dictionary represents a single point of route.
Section example:
[3GvIAP01_Way]
TAKEOFF 193373.53 99288.17 0 0 &0
TRIGGERS 0 10 20 0
NORMFLY_401 98616.72 78629.31 500.00 300.00 &0 F2
TRIGGERS 1 1 25 5 500
NORMFLY 63028.34 42772.13 500.00 300.00 r0100 1 &0
GATTACK 99737.30 79106.06 500.00 300.00 0_Chief 0 &0
GATTACK 74338.61 29746.57 500.00 300.00 4_Static 0 &0
GATTACK 82387.92 51163.75 500.00 300.00 0_Rocket 0 &0
LANDING_104 185304.27 54570.12 0 0 &1
Output example:
{
'flight_route_3GvIAP01': [
FlightRouteTakeoffPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.takeoff_normal,
pos=Point3D(193373.53, 99288.17, 0.0),
speed=0.0,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
delay=10,
spacing=20,
),
FlightRoutePatrolPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.patrol_triangle,
pos=Point3D(98616.72, 78629.31, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=Formations.echelon_right,
radio_silence=False,
patrol_cycles=1,
patrol_timeout=1,
pattern_angle=25,
pattern_side_size=5,
pattern_altitude_difference=500,
),
FlightRouteAttackPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.air_attack,
pos=Point3D(63028.34, 42772.13, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
target_id='r0100',
target_route_point=1,
),
FlightRouteAttackPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.ground_attack,
pos=Point3D(99737.30, 79106.06, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
target_id='0_Chief',
target_route_point=0,
),
FlightRouteAttackPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.ground_attack,
pos=Point3D(74338.61, 29746.57, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
target_id='4_Static',
target_route_point=0,
),
FlightRouteAttackPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.ground_attack,
pos=Point3D(82387.92, 51163.75, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
target_id='0_Rocket',
target_route_point=0,
),
FlightRoutePoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.landing_straight,
pos=Point3D(185304.27, 54570.12, 0.00),
speed=0.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=True,
),
]
}
There are 4 different types of route points. Each of them has several subtypes. All of them are described as types of route points.
Each point has type, X, Y, and Z coordinates and speed. They also tell about radio silence and can have information about air formation.
5.20.1. Take-off¶
Take-off includes taxiing and instant take-off. Aircrafts in take-off can be
aligned as normal, pair or inline. The latter two work off as
runway take-off; i.e. planes take-off in the direction of the next waypoint.

You can also set the distance between planes on the ground. You can also delay the take-off.
If you set normal takeoff, plane position will be snapped to runway as usual if the waypoint is less than 1250 m away from the runway. However, flight will respect any delay that was set.
You can also specify all of those parameters for carrier take-off, but all except the time delay will be ignored.
Definition example:
TAKEOFF_003 80156.47 47263.58 0 0 &0
TRIGGERS 0 2 20 0
Output example:
FlightRouteTakeoffPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.takeoff_in_line,
pos=Point3D(80156.47, 47263.58, 0.0),
speed=0.0,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
delay=2,
spacing=20,
)
Take-off points are defined by
FlightRouteTakeoffPoint.
Let’s examine defined lines:
TAKEOFF_003Type of route point (inline take-off).
Output path: typeOutput type: complex constant route point types 80156.47X coordinate.
Output path: pos.xOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 47263.58Y coordinate.
Output path: pos.yOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 0Z coordinate.
Output path: pos.zOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 0Speed.
Output path: speedOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number &0Tells whether radio silence is enabled for this route point.
Output path: radio_silenceOutput type: boolOutput value: Trueif&1,Falseotherwise
Note
TRIGGERS line is not present for normal take-off
TRIGGERS- Tells that this line contains additional options for previous one.
0- Is not used for take-off.
2Time delay (in minutes)
Output path: delayOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number 20Distance between aircrafts (in meters).
Output path: spacingOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number 0- Is not used for take-off.
5.20.2. Normal flight¶
Normal flight mode includes cruising, patrolling, and
artillery spotter.
Patrolling will establish circling movement in a particular pattern (triangle, square, etc.). You can adjust orientation of the pattern (direction of first waypoint in the pattern), side size (in km) and altitude difference from waypoint to waypoint (climbing or descending pattern).
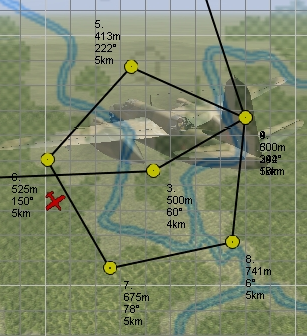
If number of cycles or timer are set, they will tell AI when to exit the pattern and continue with subsequent waypoints. They work as OR logic, so whichever comes first will make the AI exit the cycle. Zero value for either of the two parameters means that this trigger is ignored.
Waypoints with type artillery spotter have such parameters as: number of
cycles, timer, direction and side size. However, they do not have any effect.
Definition example:
NORMFLY_401 98616.72 78629.31 500.00 300.00 &0 F2
TRIGGERS 1 1 25 5 500
Output example:
FlightRoutePatrolPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.patrol_triangle,
pos=Point3D(98616.72, 98616.72, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=Formations.echelon_right,
radio_silence=False,
patrol_cycles=1,
patrol_timeout=1,
pattern_angle=25,
pattern_side_size=5,
pattern_altitude_difference=500,
)
Patrol points are defined by
FlightRoutePatrolPoint. In other
cases (normal flight and artillery spotter)
FlightRoutePoint is used.
Let’s examine defined lines:
NORMFLY_401Type of route point (patrolling using triangle pattern).
Output path: typeOutput type: complex constant route point types 98616.72X coordinate.
Output path: pos.xOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 98616.72Y coordinate.
Output path: pos.yOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 500.00Z coordinate.
Output path: pos.zOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 300.00Speed.
Output path: speedOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number &0Tells whether radio silence is enabled for this route point.
Output path: radio_silenceOutput type: boolOutput value: Trueif&1,FalseotherwiseF2Type of air formation (echelon right).
Output path: formationOutput type: complex constant air formations or None
Note
TRIGGERS line is not present for normal flight
TRIGGERS- Tells that this line contains additional options for previous one.
1[1]Number of cycles to repeat.
Output path: patrol_cyclesOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number 2[1]Timeout (in minutes).
Output path: patrol_timeoutOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number 25[1]Angle of pattern (in degrees).
Output path: pattern_angleOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number 5[1]Size of pattern’s side (in km).
Output path: pattern_side_sizeOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number 500[1]Altitude difference (in meters).
Output path: pattern_altitude_differenceOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number
5.20.3. Attack¶
There are 2 kinds of way points which tell AI to attack other units: attack
ground units and attack air units. Both of them have same parameters, but
different types. Former one is defined as GATTACK and the latter as
NORMFLY.
Note
Yes, waypoints which tell AI to attack air units has type NORMFLY, just
if it is a normal flight point. This is misleading, so route point types
define this type as X_AIR_ATTACK, where X tells that this is a fake
type.
A target is any destroyable object: aircraft, moving vehicle, artillery, rocket, static object, etc.
Definition example:
NORMFLY 63028.34 42772.13 500.00 300.00 r0100 1 &0
GATTACK 99737.30 79106.06 500.00 300.00 0_Chief 0 &0
Output example:
[
FlightRouteAttackPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.air_attack,
pos=Point3D(63028.34, 42772.13, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
target_id='r0100',
target_route_point=1,
),
FlightRouteAttackPoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.ground_attack,
pos=Point3D(99737.30, 79106.06, 500.00),
speed=300.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=False,
target_id='0_Chief',
target_route_point=0,
),
]
Attack points are defined by
FlightRouteAttackPoint.
Let’s examine the second line:
GATTACKType of route point (attack ground unit).
Output path: typeOutput type: complex constant route point types 99737.30X coordinate.
Output path: pos.xOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 79106.06Y coordinate.
Output path: pos.yOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 500.00Z coordinate.
Output path: pos.zOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 300.00Speed.
Output path: speedOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 0_ChiefID of the unit to attack.
Output path: target_idOutput type: strOutput value: original string value 0Waypoint number of the unit to attack (not relevant for static objects).
Output path: target_route_pointOutput type: intOutput value: original value converted to integer number &0Tells whether radio silence is enabled for this route point.
Output path: radio_silenceOutput type: boolOutput value: Trueif&1,Falseotherwise
5.20.4. Landing¶
For landing you can choose one of the 5 landing patterns:
- right;
- left;
- short right;
- short left;
- straight in.
Left pattern is the default pattern used in versions of the game before
4.12. The straight in landing is rather tricky to get correct and can cause
planes to crash into each other. You can set several flights with different
pattern to land on the same airfield. AI seems to handle this fairly well, but
there are no guarantees that they will not collide. All settings are ignored if
the flight is landing on a carrier (i.e. they use default left pattern).
Definition example:
LANDING_104 185304.27 54570.12 0 0 &1
Output example:
FlightRoutePoint(
type=RoutePointTypes.landing_straight,
pos=Point3D(185304.27, 54570.12, 0.00),
speed=0.00,
formation=None,
radio_silence=True,
)
Landing points do not have special parameters and they are defined by
FlightRoutePoint.
Description:
LANDING_104Type of route point (landing using
straightpattern).Output path: typeOutput type: complex constant route point types 185304.27X coordinate.
Output path: pos.xOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 54570.12Y coordinate.
Output path: pos.yOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 0Z coordinate.
Output path: pos.zOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number 0Speed.
Output path: speedOutput type: floatOutput value: original value converted to float number &1Tells whether radio silence is enabled for this route point.
Output path: radio_silenceOutput type: boolOutput value: Trueif&1,Falseotherwise
Footnotes:
| [1] | For patrol points only. |